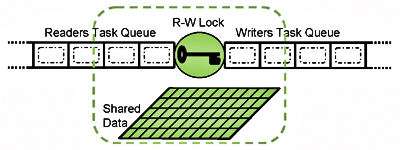
A reader-writer lock is a lock which will allow multiple concurrent readers but only one writer. A reader-writer lock can be significantly more efficient than a standard mutex if reads on your shared memory far outnumber writes.
Reader-writer locks naturally fit together with caches, as caches are only effective if reads far outnumber writes.
Here is a general pattern for using a reader-writer lock with a cache:
- Acquire a reader lock.
- Check the cache for the value. If it exists, save the value and go to step 8.
- Upgrade the reader lock to a writer lock.
- Check the cache for the value. If it exists, save the value and go to step 7.
- Calculate the value (expensive, otherwise we wouldn’t cache it)
- Insert the value into the cache.
- Release the writer lock.
- Release the reader lock.
- Return the value.
The reason why we have to check the cache for the value again in step (4) is because of the following possibility (assume step 4 doesn’t exist):
Read more...